
We are committed to helping you protect your sight for a lifetime. Regular comprehensive eye exams are the foundation of your long-term eye health. They ensure any issues are detected and dealt with early, optimising your chance of preserving your vision and eye health.
A comprehensive eye exam goes far beyond just checking your vision for glasses or contact lens prescriptions. We’ll also check for eye diseases and other potential vision issues before symptoms appear and they become harder to treat.
Generally, we recommend comprehensive eye exams annually for most adults and children, although this depends on risk factors, such as a family history of certain conditions, age, or other health conditions. If you have conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, or a family history of eye disease, more frequent exams may be necessary.
Children can have their first comprehensive screening from the age of 2. This is essential for checking that their vision is developing properly and giving them the help they may need in the classroom or on the playground. Our eye exams for children assess visual acuity and eye health. Detecting issues such as squints or lazy eyes (amblyopia) enables us to deal with them promptly so that they don’t leave a lasting effect on your child’s life.
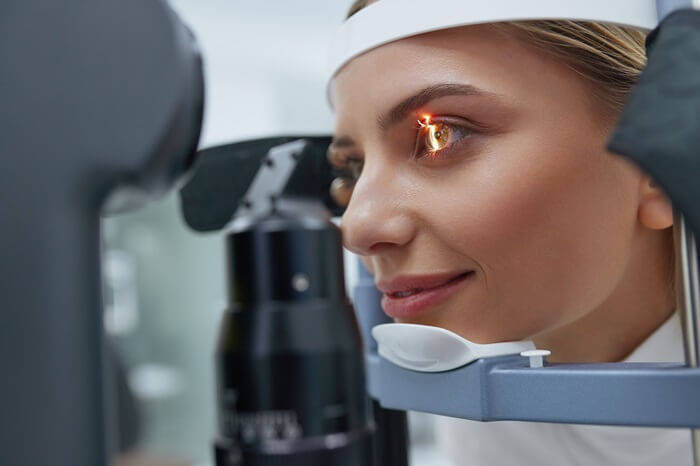
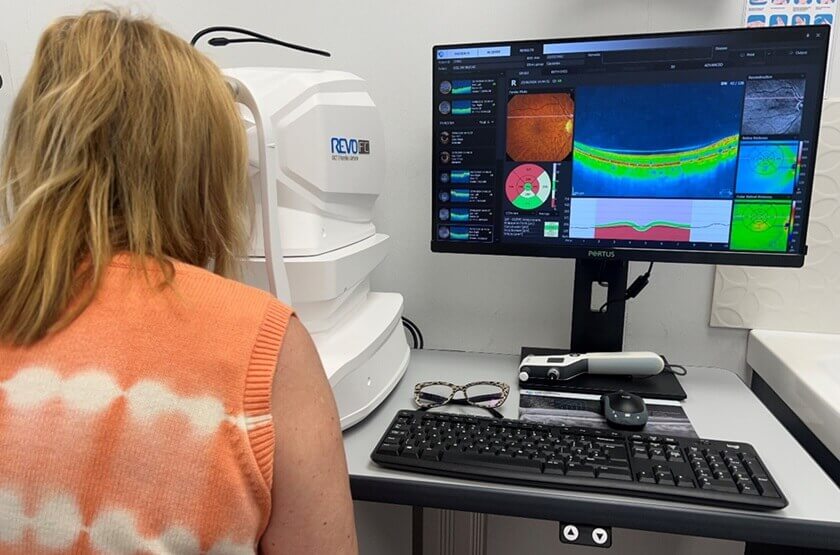
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a breakthrough imaging technology included in our comprehensive eye exams. OCT uses light waves to capture detailed cross-sectional images of your retina and optic nerve. This non-invasive procedure allows us to detect early signs of conditions like macular degeneration, glaucoma, and diabetic retinopathy, even before symptoms arise. The precision and detail of OCT provide critical insights, helping us manage and treat eye conditions effectively, ensuring you receive the best possible care.
Our comprehensive exams include several important tests using the latest eyecare technology. These include:
Our caring optometrists take the time to thoroughly evaluate your eye health and vision using these state-of-the-art diagnostic tools. We also discuss your vision needs, lifestyle, and any symptoms or eye coordination issues you may be experiencing.
Protect your eyesight with regular comprehensive eye exams. We encourage you to call us today to book your appointment.
We will do our best to accommodate your busy schedule.
94 Stoke Newington Church St,
London N16 0AP,
United Kingdom
Monday to Friday - 9:30am to 5:30pm
Wednesday and Thursday - late night until 6:30pm
Saturdays - 9:30am to 4:00pm
Sundays - Closed
© All rights reserved. Website designed and developed by OptiCommerce.